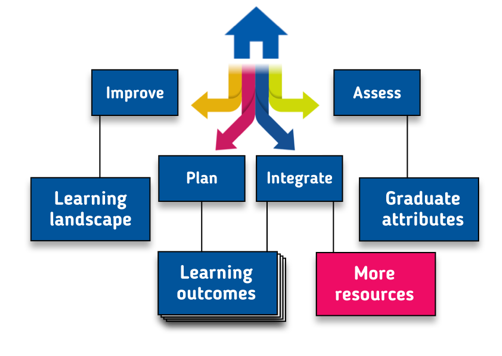
This Explorer was built to help you navigate the landscape of engineering ethics education. Choose a path depending on what you want to do: each path leads you through content such as learning outcomes, graduate attributes, and accreditation criteria, while also pointing you to supporting activities and resources linked to the content. Find your way using the map at top right or by navigating to the links in the menu bar.
These activities and resources are HOW educators can integrate engineering ethics into their teaching. Ethics is easy to include as there are ethical issues relating to virtually all aspects of engineering. This means that individual sessions on ethics can be easily integrated into an existing curriculum. Case studies which show how ethical issues arise in practical engineering settings are particularly well suited to one-off ethics sessions as well as demonstrating how ethics operates in everyday life. It is often a good idea to introduce ethics as part of the design process or through project-based learning. Design and projects provide a context in which ethical issues typically arise naturally.
Ethics provision should be regular but not necessarily frequent so introducing ethics into the curriculum need not mean a drastic reworking of course contents and timetables. The teaching of design, for example, often does not involve teaching specific design modules, but is done by bringing a design element to existing courses. Like design, engineering ethics should comprise a continuous thread woven through the undergraduate programme with students being exposed to ethical issues on a regular basis.